What is seborrhoeic eczema? - Explained by Dr. Yeung Ho Hong(楊浩康)
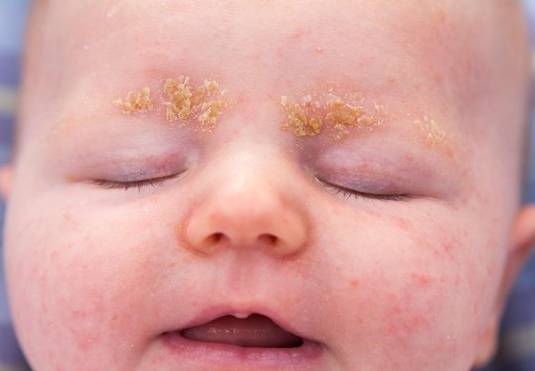
Seborrhoeic eczema is a common chronic or relapsing form of eczema/dermatitis that mainly affects the scalp and face. The cause of seborrhoeic eczema is not completely understood. It is associated with proliferation of the skin commensal Malassezia. Its metabolites cause an eczematous inflammatory reaction. Differences in skin barrier function may account for individual presentations.
There are infantile and adult forms of seborrhoeic eczema. Infantile seborrhoeic eczema affects babies under the age of 3 months and usually resolves by one year of age. Adult seborrhoeic eczema tends to begin in late adolescence. It is more common in males than in females. The following factors are sometimes associated with adult seborrhoeic eczema: oily skin, familial tendency to seborrhoeic eczema, a family history of psoriasis, immunosuppression (such as organ transplant recipient, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection), neurological disease (such as Parkinson disease, tardive dyskinesia).
Infantile seborrhoeic eczema causes cradle cap (diffuse greasy scaling). The rash may also involve axillary and inguinal skin folds. The rash is not especially itchy, so the baby often appears undisturbed by the rash.
Adult seborrhoeic eczema affects the scalp, face (nasolabial folds, behind ears, within eyebrows) and upper trunk. The patients may have rash on face, anterior chest, hairline, axillary regions submammary sites, inguinal folds and genital creases. The rash usually has minimal pruritus. Some patients may have dandruff with ill-defined localised scaly patches or diffuse scale throughout the scalp.
Seborrhoeic Eczema is a chronic, multifactorial skin disease that requires a combination of medication and daily care. Although the cause of the disease is not yet fully understood, available treatments are effective in relieving symptoms and improving skin appearance, thereby improving the quality of life of patients. For patients with recurring or severe symptoms, early treatment by a professional dermatologist is recommended to develop a customized treatment plan to achieve the best results.
參考文獻:
1. Bolognia, J., Schaffer, J. V., & Cerroni, L. (2018). Dermatology (4th ed.). Elsevier.
2. Gupta, A. K., & Versteeg, S. (2017). "Seborrheic Dermatitis: An Update on Epidemiology, Pathogenesis and Treatment." Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, 31(9), 1453-1461.
3. Dessinioti, C., Katsambas, A. (2013). "Seborrheic Dermatitis: Etiology, Risk Factors, and Treatment Options." Dermatologic Clinics, 31(3), 405-418.
